
Likewise, the oxidation number of H is reduced from +1 to zero, so hydrogen is reduced in this reaction and Mg is referred to as a reducing agent.Ģ. It's oxidation number increases, so Mg is oxidized in this reaction and we refer to HCl as an oxidizing agent or an oxidizer. Mg goes from an oxidation state of 0 to +2. numbers because that's hydrogen in its elemental form. Mg is a group 2A element, so it has a +2 oxidation number, and the hydrogens of H 2 have zero ox. number, and the Cl gets a -1 because the sum of oxidation numbers of a neutral compound has to be zero. Hydrogen bound to a nonmetal has a +1 ox. In this reaction, the Mg is presumed to be in its metallic elemental form because it doesn't have a charge, so its oxidation number is zero. By the way, the reaction doesn't need to be balanced for this oxidation-number analysis, but this one is. In order to tell if a reaction is a reduction-oxidation ( redox) reaction, we assign oxidation numbers to each atom. Hydrogen exists as a diatomic gas in its elemental form. In the case of Mg, if no charge and no state are shown, we have to assume it's metallic Mg. For example, Mg, H 2, Ar and Fe (s) are all examples of atoms in their elemental states.
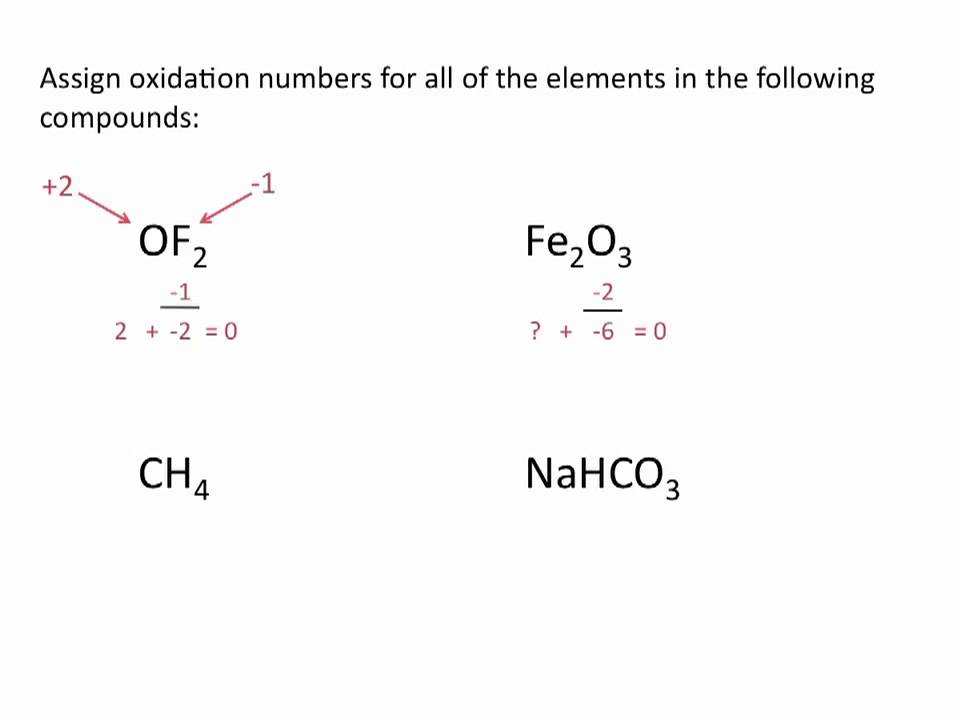

I'll go through them here, but they're recapped in the table below. There are agreed-upon rules for assigning oxidation numbers. If electrons are exchanged, that will be reflected in the difference in oxidation number of atoms on the right and left side of the chemical equation, and the reaction is called a redox (reduction-oxidation) reaction. Reactions can proceed with or without the exchange of electrons.

They represent, loosely, the number of electrons available for shuffling around during the course of a reaction. Oxidation numbers are made-up or hypothetical numbers assigned to each atom in a reaction, individual or within a molecule.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
